The quest for efficient and environmentally friendly power generation methods is paramount in the energy industry. One such technology that has gained widespread recognition for its effectiveness and versatility is the circulating fluidized bed boiler (CFB). Known for its ability to burn a variety of fuels while reducing emissions, the CFB boiler is a cornerstone of modern power generation and industrial heating systems.
In this article, we’ll explore the basics of the circulating fluidized bed boiler, how it works, its benefits, and why it’s becoming a favored choice in industries looking to balance energy production with environmental responsibility.
What is a CFB?
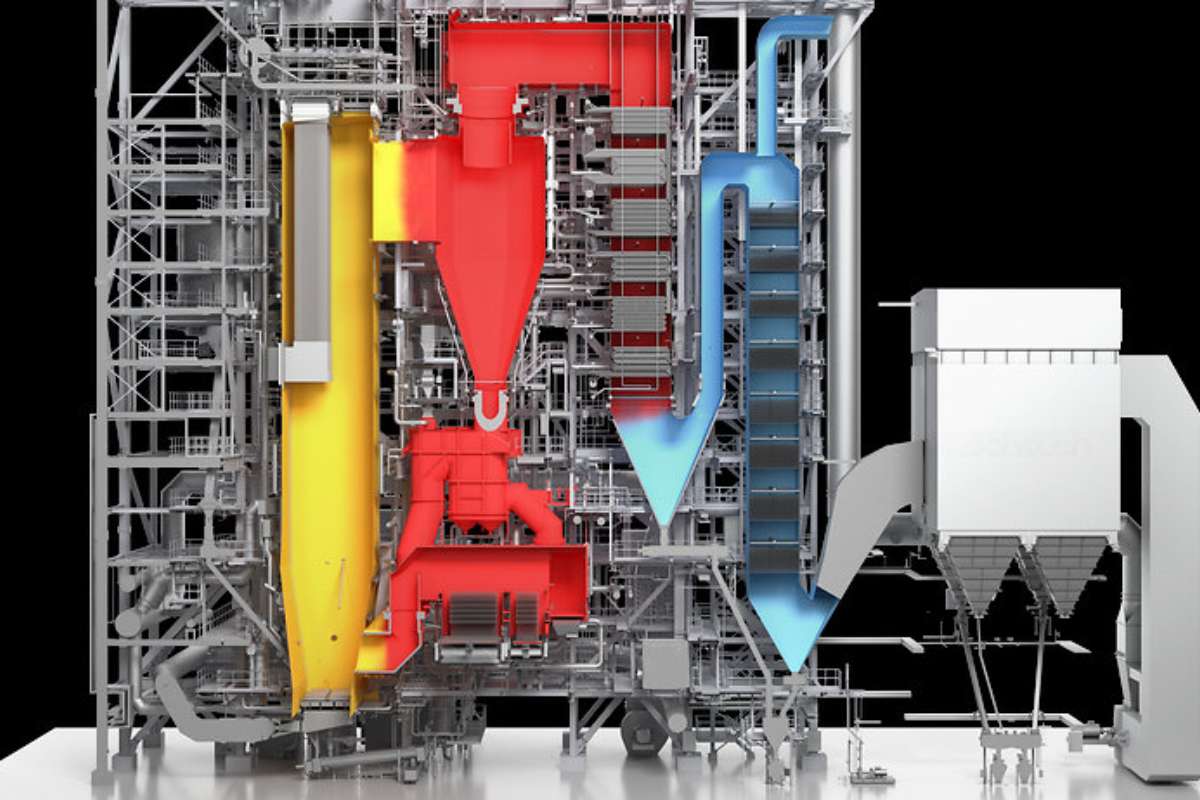
A circulating fluidized bed boiler is a type of combustion system that burns fuel in a fluidized bed of air and solid particles, typically consisting of coal, biomass, or other fuels. The term “fluidized” refers to how the solid particles behave like a fluid due to the continuous flow of air. These solid particles, such as sand or ash, are suspended in the air current, creating optimal conditions for combustion.
Unlike traditional boilers, which burn fuel at a fixed rate, the CFB is designed to circulate the fuel particles throughout the combustion chamber. This circulation allows for more efficient heat transfer and ensures a more uniform burn, which translates to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
How Does a CFB Work?
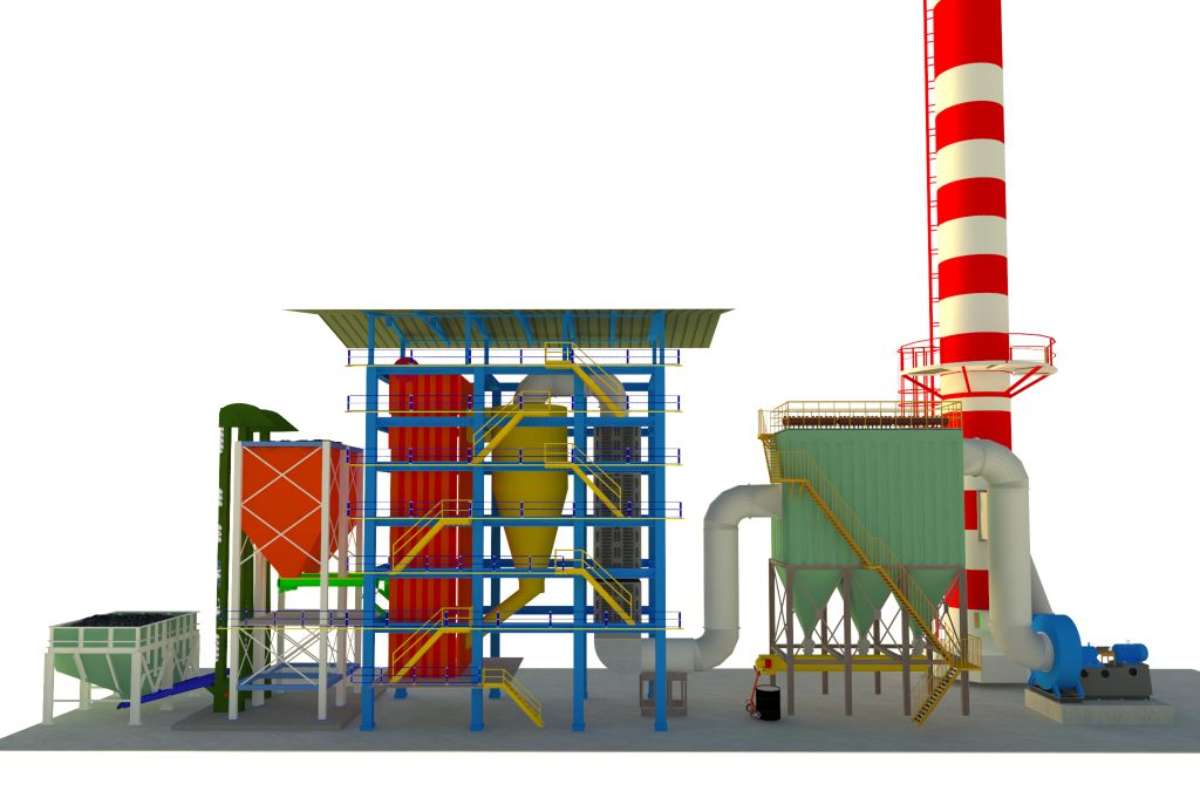

The working principle of a circulating fluidized bed boiler revolves around the fluidization of fuel particles within the combustion chamber. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
1. Fuel Introduction
Fuel is introduced into the combustion chamber along with inert particles (often sand or limestone) that help to absorb heat and facilitate combustion.
2. Fluidization
High-velocity air is blown from beneath the combustion bed, causing the solid fuel particles to become suspended or “fluidized.” This creates a dynamic, fluid-like environment where the fuel can combust more evenly and at lower temperatures compared to traditional boilers.
3. Combustion
The fuel combusts as it moves through the chamber, while the fluidized bed absorbs heat and stabilizes the temperature. This results in a more consistent and complete burn.
4. Recirculation
After combustion, the flue gases and entrained particles (ash, unburned fuel, and inert material) are separated. The solid particles are then recirculated back into the bed to ensure complete combustion, while the flue gases are released through exhaust systems after being cleaned.
5. Heat Recovery
The heat generated in the combustion process is transferred to water or steam in the boiler’s heat exchangers. This steam can then be used to power turbines for electricity generation or provide heat for industrial processes.
Advantages of CFB
The CFB stands out from other boiler types due to its numerous advantages, particularly in terms of fuel flexibility and environmental impact. Here are some key benefits:
1. Fuel Flexibility
CFB boilers can burn a wide variety of fuels, including coal, biomass, and waste materials. This flexibility allows industries to use locally available fuels, reducing dependency on expensive imported fuels.
2. Lower Emissions
One of the most significant advantages of a circulating fluidized bed boiler is its ability to reduce harmful emissions, particularly sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). The lower combustion temperature and the use of limestone in the bed help to capture sulfur, while the staged combustion process reduces NOx formation.
3. Higher Efficiency
CFB boilers operate at lower combustion temperatures than traditional boilers, resulting in better heat transfer and reduced fuel consumption. The recirculation of solid particles also ensures that more fuel is fully combusted, leading to higher overall efficiency.
4. Reduced Maintenance Costs
Due to their robust design and efficient combustion process, CFB boilers experience less wear and tear than conventional boilers, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repairs.
5. Environmental Sustainability
The ability to burn renewable fuels, such as biomass, and waste materials means that CFB boilers can play a significant role in reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainable energy production.
Applications of CFB
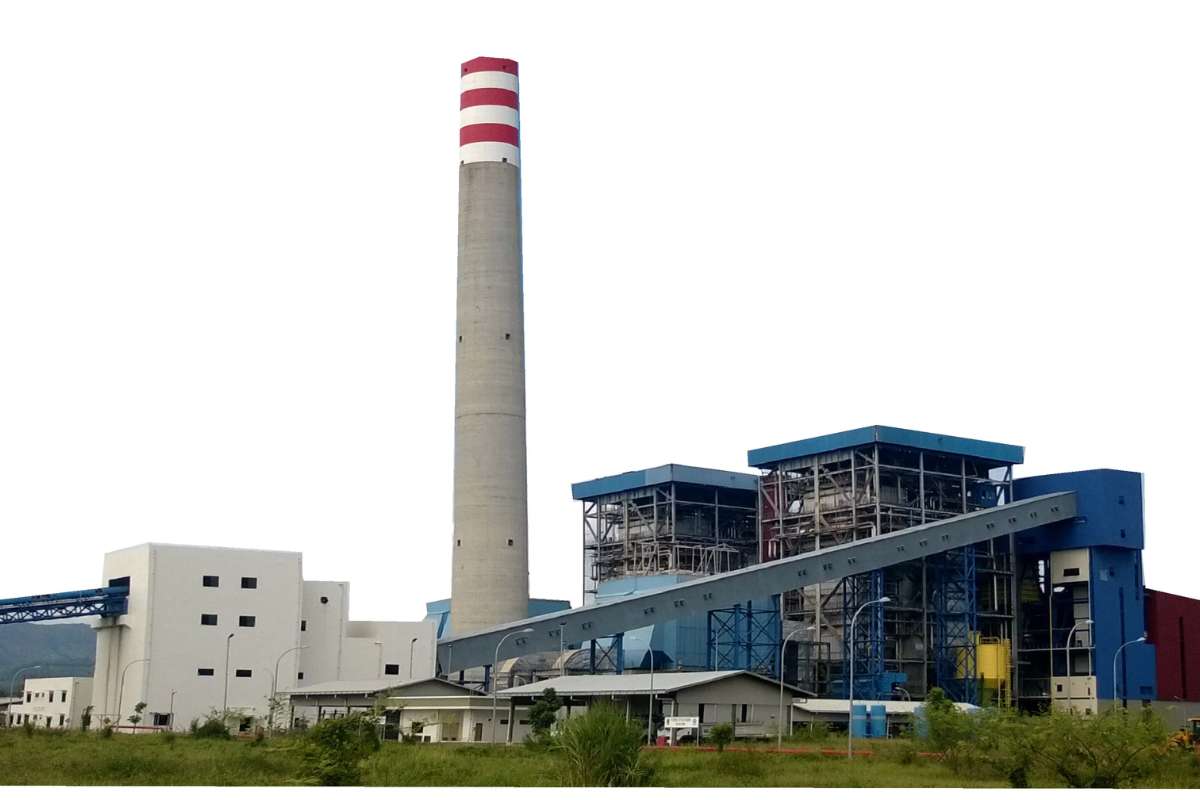

The versatility of the CFB has made it a popular choice across various industries, particularly those that require reliable and efficient heat generation. Some common applications include:
1. Power Plants
CFB technology is widely used in coal-fired power plants to produce electricity. Its ability to reduce emissions while burning a wide range of fuels makes it an attractive option for power producers.
2. Industrial Heating
Many industries, such as cement, steel, and chemical manufacturing, rely on CFB boilers to provide the necessary heat for their processes. The fuel flexibility of these boilers allows industries to optimize fuel costs and reduce emissions.
3. Waste-to-Energy Plants
CFB boilers can burn waste materials such as municipal solid waste (MSW), agricultural residues, and industrial byproducts. This makes them a valuable asset in waste-to-energy plants, where the goal is to generate energy while reducing landfill waste.
4. Biomass Power Plants
As the demand for renewable energy grows, biomass power plants are increasingly using CFB technology to burn organic materials like wood chips, agricultural waste, and forestry residues. CFB boilers offer an efficient and environmentally friendly way to harness biomass energy.
Challenges and Considerations
While the CFB offers many benefits, it’s important to be aware of some of the challenges associated with this technology:
- Initial Costs: CFB boilers tend to have higher upfront capital costs compared to traditional boiler systems. However, the long-term operational savings due to lower fuel costs, reduced emissions, and less maintenance can offset these initial expenses.
- Operational Complexity: The technology behind CFB boilers is more complex than conventional boilers, which may require more skilled operators and a better understanding of fluidized bed dynamics.
- Space Requirements: Due to the need for large combustion chambers and recirculation systems, CFB boilers typically require more physical space than other boiler types. This can be a challenge for facilities with limited space.
The Future of Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers

As industries around the world strive to meet stricter environmental regulations and reduce their carbon footprints, the circulating fluidized bed boiler will likely continue to play a crucial role in the future of energy production. Innovations in CFB technology, such as improved heat recovery systems, more efficient fuel combustion, and enhanced emissions control, will further cement its position as a preferred option for sustainable energy.
Moreover, the global shift towards renewable energy sources, such as biomass and waste-to-energy solutions, will drive the demand for flexible and efficient boiler systems like CFB boilers. As these trends continue, we can expect CFB technology to evolve and adapt to meet the growing needs of a cleaner and greener energy landscape.
Conclusion
The circulating fluidized bed boiler is a proven and versatile technology that offers numerous advantages in terms of fuel flexibility, emission reduction, and energy efficiency. Whether in power plants, industrial heating, or waste-to-energy applications, CFB boilers are playing a vital role in meeting the energy demands of today while addressing environmental concerns.
As industries and governments continue to prioritize sustainability, the circulating fluidized bed boiler will remain at the forefront of innovative, eco-friendly energy solutions, ensuring a cleaner and more efficient future for power generation.