(Source – iACS – HVAC Control Specialists).
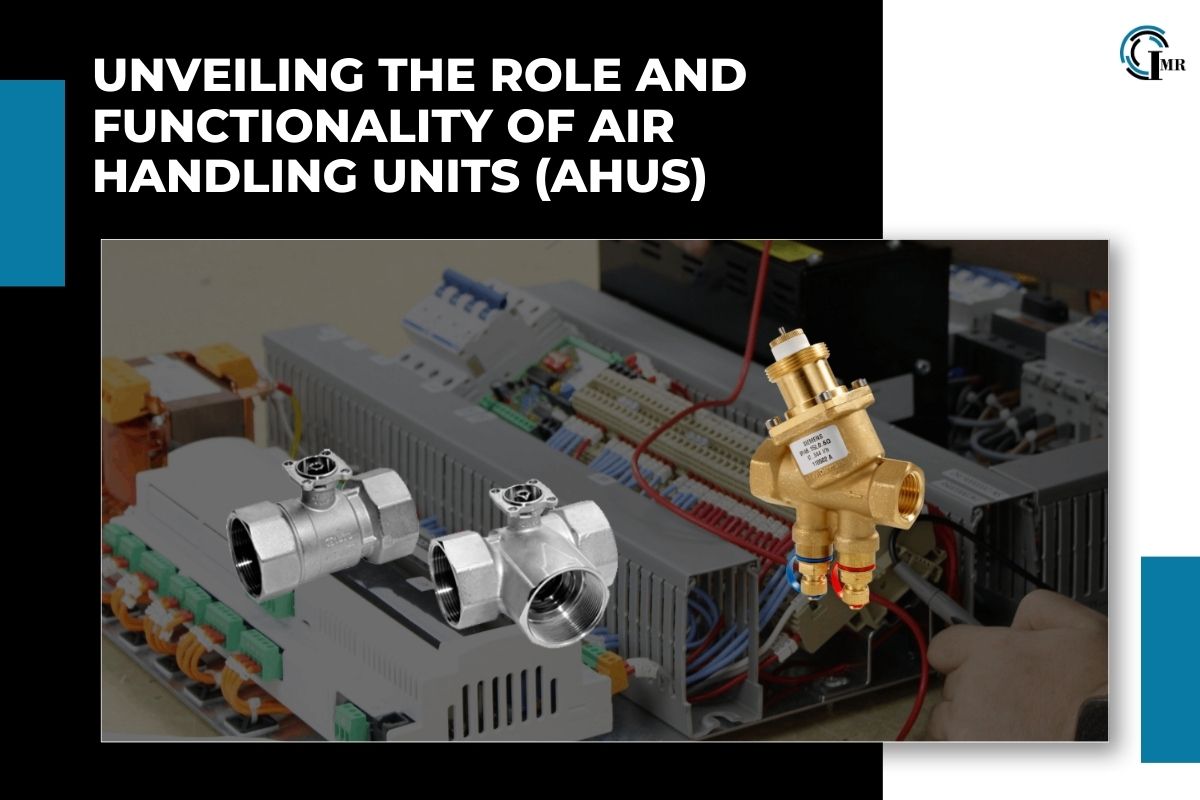
Air handling units (AHUs) are critical components of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, playing a pivotal role in maintaining indoor air quality, temperature control, and comfort in various commercial, industrial, and residential settings. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the fundamentals, components, operation, applications, and benefits of AHUs, shedding light on their significance in modern building design and HVAC engineering.
Understanding Air Handling Units
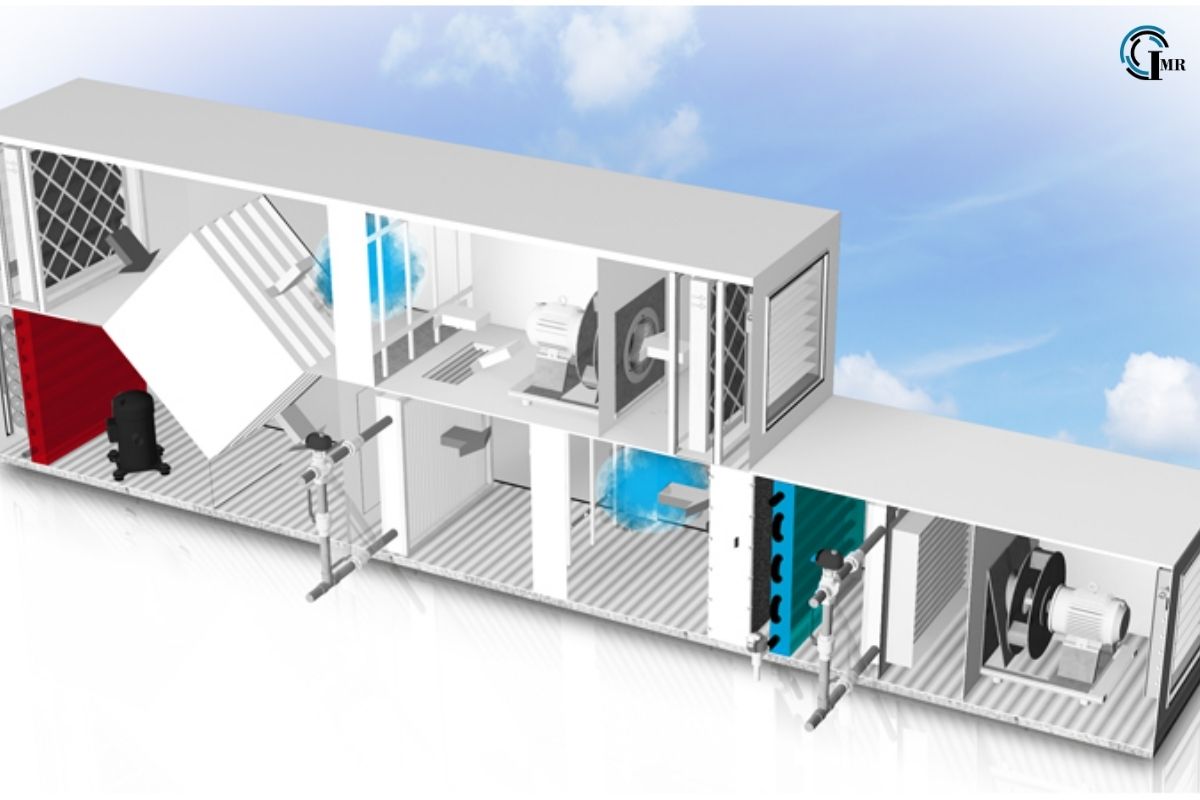
Air handling units, often referred to as air handlers, are complex assemblies of components designed to circulate, filter, heat, cool, humidify, dehumidify, and distribute air within a building. These units are typically housed in mechanical rooms or rooftop enclosures, where they receive outdoor air and condition it before distributing it to different zones or spaces through ductwork.
Components of Air Handling Units
AHUs consist of several key components, each serving a specific function in the air treatment process:
1. Fans: Fans are responsible for moving air through the AHU and into the building’s ductwork. They come in various configurations, including centrifugal fans and axial fans, and can be equipped with variable speed drives (VSDs) for energy efficiency and airflow control.
2. Filters: Air filters remove dust, pollen, allergens, and other particulate matter from the incoming air, improving indoor air quality and protecting downstream components from contamination. Filters are classified based on their efficiency rating, ranging from basic panel filters to high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters.
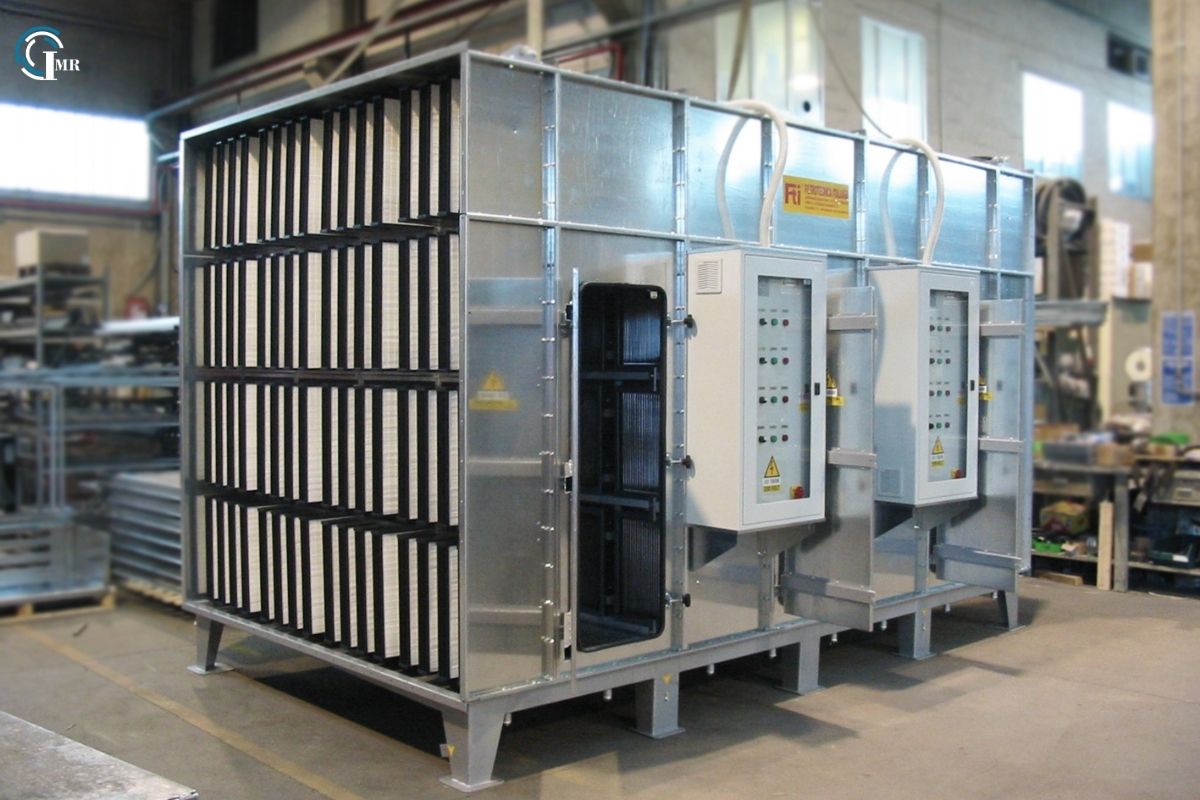

3. Heating and Cooling Coils: Heating and cooling coils, also known as coils or heat exchangers, regulate the temperature of the air passing through the AHU. Heating coils use hot water or steam, while cooling coils use chilled water or refrigerants to heat or cool the air, respectively.
4. Humidifiers and Dehumidifiers: Humidifiers add moisture to the air to prevent dryness, while dehumidifiers remove excess moisture to maintain optimal humidity levels. These components are essential for comfort control and preventing issues such as mold growth and condensation.
5. Dampers: Dampers are adjustable valves or louvers located within the AHU’s ductwork, regulating the flow of air to different zones or spaces. They can be manually operated or motorized and are used for temperature zoning and energy conservation.
Operation of Air Handling Units
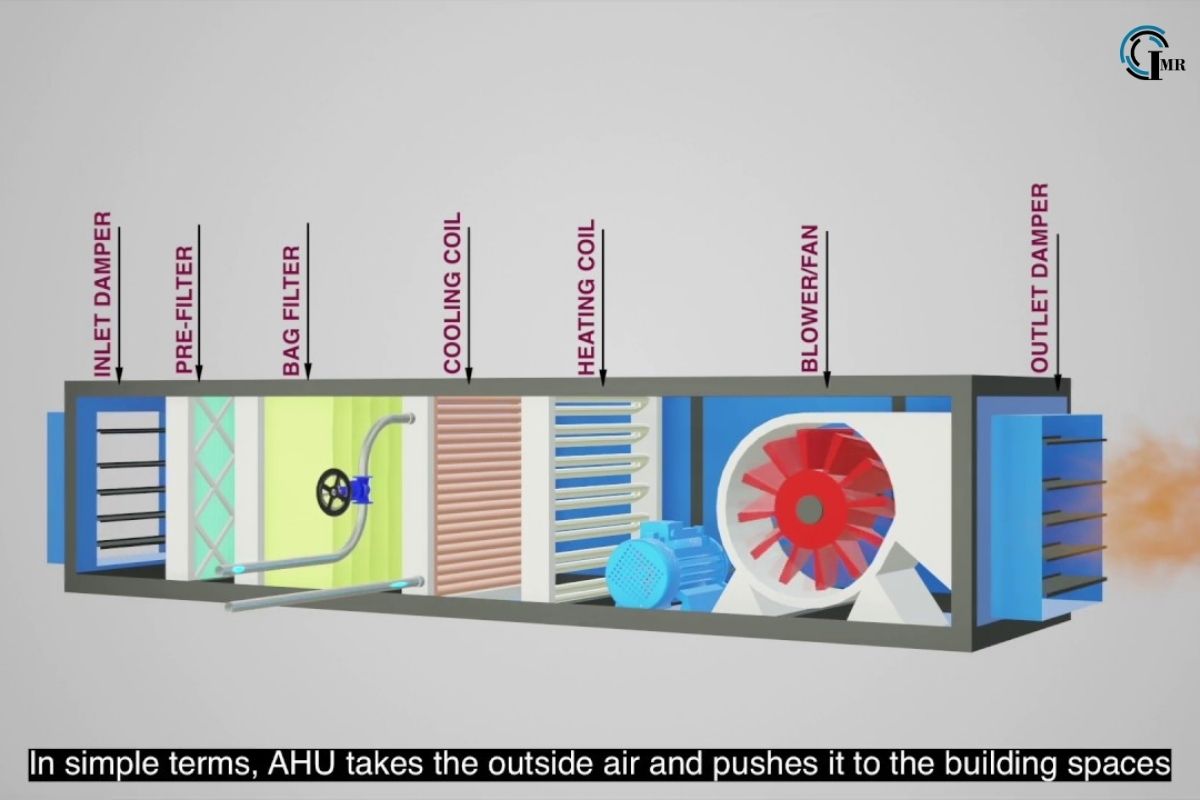
The operation of AHUs involves several stages, including air intake, filtration, heating or cooling, humidification or dehumidification, mixing, and distribution. The sequence of operations is controlled by a central control system or building automation system (BAS), which monitors environmental conditions and adjusts the AHU’s settings accordingly.
Applications of Air Handling Units
Air handling units have diverse applications across various industries and building types:
Commercial Buildings: AHUs are commonly used in office buildings, retail stores, hotels, and restaurants to provide conditioned air for occupants’ comfort and well-being. They are also integral to maintaining indoor air quality in healthcare facilities, schools, and public buildings.
Industrial Facilities: In industrial settings such as manufacturing plants, warehouses, and cleanrooms, AHUs play a critical role in controlling humidity, temperature, and airborne contaminants to ensure product quality, process efficiency, and worker safety.
Data Centers: Data centers rely on precision air conditioning systems with AHUs to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels for the reliable operation of sensitive electronic equipment. AHUs with redundant components and advanced filtration are essential for preventing downtime and equipment failures.
Residential HVAC Systems: In residential buildings, AHUs are part of central HVAC systems that provide heating, cooling, and ventilation to individual dwelling units. These units enhance indoor air quality, energy efficiency, and occupant comfort in homes and apartments.
Benefits of Air Handling Units
The adoption of AHUs offers numerous benefits for building owners, operators, and occupants:
Improved Indoor Air Quality: By filtering and conditioning outdoor air, AHUs remove airborne pollutants, allergens, and contaminants, improving indoor air quality and creating a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment.
Energy Efficiency: High-efficiency AHUs equipped with variable speed drives, energy recovery systems, and advanced controls help reduce energy consumption and operating costs while optimizing HVAC system performance.
Enhanced Comfort and Productivity: Well-designed AHUs deliver precise temperature and humidity control, ensuring occupant comfort and productivity in commercial, industrial, and residential spaces.
Flexibility and Adaptability: AHUs can be customized and configured to meet the specific requirements of different building types, climates, and applications, providing flexibility and adaptability in HVAC system design and operation.
Conclusion
Air handling units play a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality, comfort, and energy efficiency in buildings of all types and sizes. From commercial offices and industrial facilities to residential homes and data centers, AHUs are indispensable components of modern HVAC systems. By effectively filtering, conditioning, and distributing air, AHUs create healthier, more comfortable, and more productive indoor environments while optimizing energy use and operating costs. As the demand for sustainable and high-performance buildings continues to grow, the importance of air-handling units in achieving these goals cannot be overstated.